
ACHIEVEMENTS
Significant contributions have been made by the Division of Seed Science and Technology in the area of seed research and human resource development. The highlights of these achievements are as follows:
Role of quality seed on productivity
· Based on three years study in the division, it was established that high quality/ certified seed gave a yield advantage of 10-15% over farmers saved seed.
· It was also established that farmers should replace the quality/certified seed every 3 years in self-pollinated crops and every two years in cross and often cross-pollinated crops.
Isolation distance for seed production
· Isolation distance for foundation seed production in Pearl millet can be reduced from 1000m to 500m with border rows of male parent. Besides, the isolation distance requirements for pigeon pea, maize, mustard, wheat and paddy were also determined.
· Based on field trials conducted by the scientists of this Division at New Delhi, Hisar, Pantnagar and Pusa (Bihar) consecutively for 3 years, it has been proved that chlamydospores of Ustilago segetum var. tritici, causal pathogen of loose smut of wheat, do not travel beyond 75m. So, isolation distance can be reduced from 150m to 100m. However, this again needs national level validation.

|
Loose smut of wheat |
Hybrid seed production technology
· Hybrid seed production technology in rice has been standardized and refined by this Division which has made to realize the yield of 2.5 to 3.0 t/ha from earlier 1.5 t/ha.
· Standardized the application of 90 g GA3 and 1% boric acid per ha for better stigma exertion and receptivity in male sterile rice plants.
· Developed hybrid seed production technology of maize, cauliflower, solanaceous and cucurbitaceous vegetables.
Seed storage
· Based on data on relative humidity (RH) and temperatures for thirty years, places in India were classified as good, moderate and poor for seed storage. It was concluded that places where the mean RH does not exceed 70% for more than 3 months and mean temperature does not exceed 30 0C for more than 4 months in a year, are safe for storing seeds having moderate to good longevity.
· Most of the high value vegetable seeds are poor storers, losing germination below the certification level within one season. Results of a well-planned experiment revealed that by drying seeds to below 6% moisture and packing in heat sealed moisture resistant containers, viz., polylined aluminum foil, polyester or polythene (700 gauge) packets (leaving minimum air space), the germination standards could be maintained up to two to three seasons at ambient temperatures of Delhi.
· The mechanism of seed ageing, where increased leakage of water-soluble sugars and electrolytes due to enhanced membrane permeability, was identified in several crops.
· The water absorption properties and free radical quenching mechanism controlling the enzymatic and non-enzymatic lipid peroxidation were identified in oil rich crop species.
· The different nature and magnitude of molecular alterations resulting from natural and accelerated ageing were found in maize, soybean and safflower seeds.
· Identification of better storable and high vigour QPM inbred: Two better storable inbreds, MGU-QPM-16 and MGU-QPM-20 were identified having >90% germination after 12 months of ambient storage and >60% after 18 months. They also possess high vigour, with >70% normal seedlings after 7 days of accelerated ageing.
· Physio-chemical basis for faster deterioration in QPM inbred: The more rapid decline in the viability of the poor storer QPM inbred can be ascribed to heightened lipid oxidation (MDA content) and protein carbonylation, leading to a more pronounced loss of membrane integrity (EC), increased production of volatile aldehydes, decreased activity of enzymes involved in reserve mobilization (amylases, galactosidases, proteases), and enhanced protein glycation during natural ageing.
· Developed fast aging methodology for dry seeds using elevated oxygen pressure and identified the rice Rc gene as a main regulator of seed survival under dry storage.
· Developed anoxia seed storage technology to extend rice seed storability.
Early Seedling Vigour
· Three phases were identified in the rice seed germination process and the first phase (lemma rupture) is independent of either GA or ABA. Whereas later two phases (endosperm rupture and radicle emergence) were promoted by GA and inhibited by ABA. Abundance of galactomannan hydrolyzing enzymes (Endo-β-mannanase, β-mannosidase and α-galactosidase) in dry seeds promotes earliness in rice seed germination that in turn, are promoted by GA and inhibited by ABA.
· In mature dry seeds of early germinating rice genotype, long lived transcripts that promote germination were found to be more when compared to genotypes that are intermediate and late in germination.
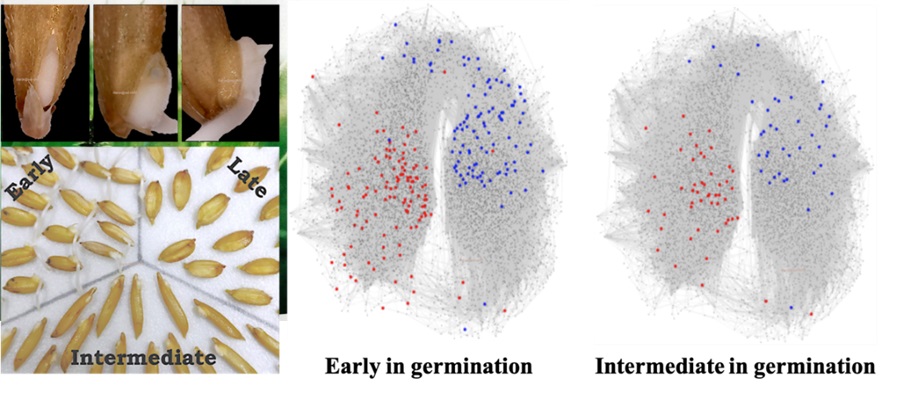
Seed dormancy
· The high temperature (30oC) induced dormancy was observed in Khesari and identified various chemical and thermal treatments to overcome it.
· Identified no relation between dormancy and longevity in Indian rice varieties and discovered the linkage between esterase and peroxidase enzymes with dormancy.
· Identified mungbean genotypes with contrasting dormancy and several marker-trait associations for seed dormancy in mungbean and rice.
· Identification of a mung bean genotype (TM 96-25) with higher dormancy levels: A mung bean genotype TM 96-25 was identified for preharvest sprouting tolerance based on pod and seed germination. This genotype consistently possesses ~60% hard seededness across years in freshly harvested seeds. The seed coat is permeable up to stage 3 (~26 DAP), and afterwards, hardness might have been attained due to lignin deposition.
Application of X-ray in seed quality monitoring
· Using X-ray radiography, the Division has done pioneering work to detect internal insect infestation, mechanical damage, emptiness, sun checks (cracks in rice endosperm). This technique has also been used for characterization and identification of paddy varieties.
Multispectral imaging
· Application of multi-spectral imaging for non-destructive, accurate, and high-throughput measurement and quantification of subtle phenotypic variation in rice seed morphological traits.
· GRAINEX technology for automated physical purity analysis in e-NAM (Electronic-National Agricultural Market) was developed by the Division of Seed Science and Technology in collaboration with C-DAC, Kolkata under AgriEnIcs program. This system will bring about a transformative change in the e-NAM markets for quality-based pricing and will be helpful for more than 1,200 e-NAM connected markets.
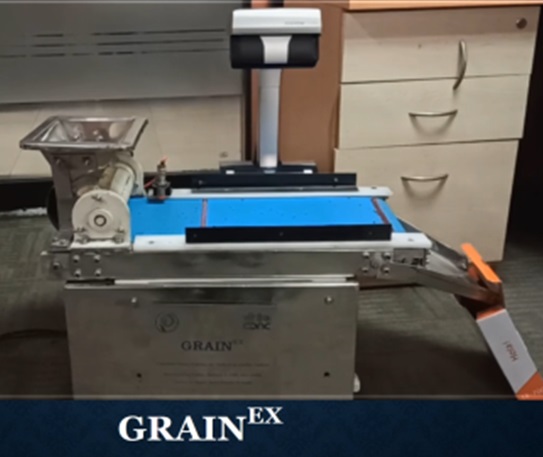

Standardization of seed quality evaluation procedures
· Standardized tetrazolium seed viability test for ragi (Eleusine coracana) and khesari (Lathyrus sativus) and germination test protocols were determined for fenugreek, red gram, khesari (Lathyrus), sesbenia, crotolaria and pasture grasses.
· Development of radicle emergence test for seed vigour estimation in pearl millet: The radicle emergence test was developed for pearl millet at 25°C, where 50 h after imbibition was highly correlated with germination of fresh and accelerated aged seed and field emergence.
Variety identification and genetic purity
· Conventionally, identification of crop varieties is based on diagnostic morphological characters of seed, seedling and mature plants. Morphological descriptors were published for the released Indian varieties of wheat and peas which are very useful for seed certification.
· The electrophoresis technique provides a rapid method for ascertaining the genetic purity or verifying the identity of a variety. The Division played a lead role in standardizing electrophoresis protocols using native (alkaline or acid) or SDS-PAGE of soluble seed proteins for distinguishing cotton, sunflower, maize, wheat, castor and rice varieties,
· Electrophoresis or iso-electrofocussing of isoenzymes, viz., esterase, peroxidase, malate dehydrogenase, glutamate dehydrogenase and glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase were found to be more accurate in distinguishing pearlmillet varieties and in establishing hybridity in several crops.
· Identified and validated protein and DNA markers to ensure the seed purity in crops like pearl millet, brinjal and tomato.
· Developed SCAR marker for ensuring A line purity against B line admixture in pearl millet.
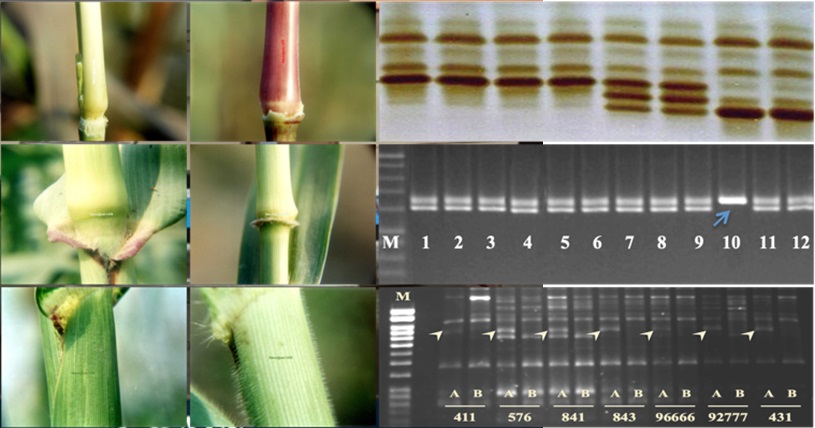
· Developed Rapid Single Seed Purity Assurance Kit (Crushed Single Seed Supernatant for PCR based seed purity assurance): The objective of the kit is to minimize the time involved in processing the DNA template for PCR reaction by directly using the single seed crushed supernatant in PCR amplification of target DNA fragment.

|
|
· Developed a suitable methodology for rice seed priming.
· Developed a suitable seed enhancement technology in the pearl millet, maize, mungbean, chickpea and soybean using nanoparticles to enhance seed germination and vigour.
· Developed seed enhancement technology in maize, cucumber and chilli to mitigate Low temperature conditions.
· Identification of native Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) for the management of major seed-borne diseases and seed quality enhancement of solanaceous and cruciferous vegetables. Developed PGPR bio-formulation through seed, soil, and seedling application.
· Application of micro nutrient loaded Nano Clay Polymer Composite (NCPC) as seed coat to enhance the respective micronutrient use efficiency in crops.
· Imbibition phases-based seed priming methodology in paddy: The water uptake by paddy seeds during imbibition was fitted using a third order polynomial regression equation to identify different phases of imbibition. After imbibition up to phase II followed by drying at 26°C enhanced the priming effect both at high and low water potentials conditions.
· Spermidine priming technique for heat stress alleviation in paddy: The seeds primed with 1 mM spermidine showed maximum tolerance to heat stress. The PEG method of spermidine priming was superior to other methods of spermidine infusion in terms of higher germination, seedling growth and vigour parameters under heat stress.
· Enhanced vigour in pearl millet after seed priming with silver nanoparticles: The silver nanoparticles (AgNP) @50 mg/L showed a significant increase in germination and vigour. This can be because of the decrease in EC and increase in antioxidants, catalase, and peroxidase activities after priming.
· Seed priming technology to improve salinity tolerance in Lentil. This involve seed treatment with combination of humic acid and silicic acid (@100 ppm + 1 mM; 16 h) and dried back to its original moisture content.
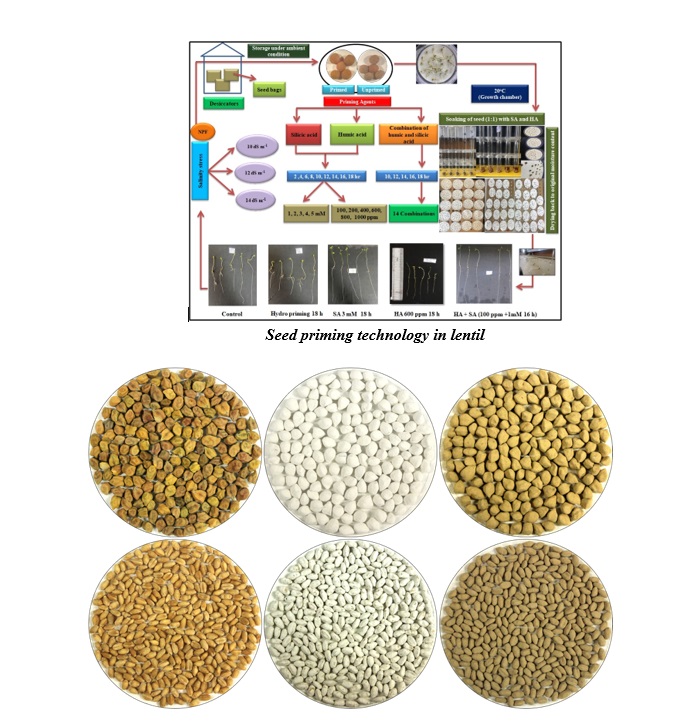
Seed priming technology in lentil
|
|
· Developed polymeric seed coats based on bioactive botanicals for maintenance of seed quality during storage and better crop establishment. (Indian Patent No. 244542 2010)
Thermotolerance studies
· Developed suitable heat stress mitigation strategy in wheat.
· Developed a methodology for thermotolerance screening of rice genotypes.
· Thermotolerance induction technology for germinating seeds and early seedling stage in paddy: The germinating seeds (1-1.5 cm radicle) and early seedling stage (7d seedlings) were given acclimation temperatures (38°C for 75 min and 42°C for 75 min, respectively) so that they can tolerate severe heat stress (48°C) even after 2 days.
HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT
The Seed Testing Laboratory in the erstwhile Botany Division of IARI started the first All India Seed Testing and Quality Control training course in 1961. This course is being organized annually and has provided the skilled trained man power for seed quality assurance and law enforcement programme of the country. In fact, the success of Indian Seed Development programme was possible due to availability of trained man power in seed technology.
Details of training programmes conducted at DSST, ICAR-IARI, New Delhi (2019- 2024)
|
Name of the training programme |
No. of participants |
Sponsored by |
|
International Workshop cum Capacity Building Training Programme on Advanced Seed Production Technologies at ICAR-IARI RS, Karnal (12 - 15 March, 2024) |
20 |
DACF&W, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, GOI and Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BEML), Germany |
|
International Workshop cum Capacity Building Training Programme on OECD Seed Certification for Seed Export at RARI, Durgapura (19-23 Feb, 2024)
|
10 |
DACF&W, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, GOI and Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BEML), Germany |
|
International Workshop cum Capacity Building Training Programme on Post-Harvest Technologies for Seed Quality Improvement at ICAR-IARI, New Delhi (28 Nov-01 Dec., 2023) |
20 |
DACF&W, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, GOI and Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BEML), Germany |
|
Seed Production and Certification of field crops (02-04 Aug, 2023) |
20 |
Govt. of Assam (ASCL and AOSCA) |
|
Seed production, testing and storage in field and vegetable crops (13-17 March, 2023) |
25 |
Self-sponsored |
|
International training cum Capacity Building Programme on “Seed Production and Quality Evaluation” (12-23 Feb, 2023) |
10 |
MoRD, GOI and AARDO |
|
Seed production and certification of field crops (14-16 Sept, 2022) |
10 |
Govt. of Assam (ASCL and AOSCA) |
|
International Capacity Building Webinar - cum -Workshop on “Seed Quality Enhancement (Mustard, Wheat and Barley)” (22-24 Sept, 2021) |
146 |
DACF&W, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, GOI (Indo-German Cooperation on Seed Sector Development) |
|
International Online Training Programme on “Seed Production and Quality Evaluation” (28 July–7 Aug, 2021) |
81 |
AARDO Secretariat |
|
International Capacity Building Webinar - cum -Workshop on “Seed Testing for Quality Assurance (Mustard, Wheat and Barley)” (6 - 9 July, 2021) |
131 |
DACF&W, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, GOI (Indo-German Cooperation on Seed Sector Development) |
|
International Capacity Building Webinar - cum -Workshop on “Post-Harvest Technologies for Better Seed Quality (Potato, Wheat and Barley)” (15-17 March, 2021) |
61 |
DACF&W, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, GOI (Indo-German Cooperation on Seed Sector Development) |
|
International Capacity Building Webinar - cum -Workshop on “OECD Seed Certification (Mustard, Wheat and Barley)” (8-12 Feb, 2021) |
172 |
DACF&W, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, GOI (Indo-German Cooperation on Seed Sector Development) |
|
International Capacity Building Webinar - cum -Workshop on “Seed Production (Mustard, Wheat and Barley” (12-14 Jan, 2021) |
57 |
DACF&W, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, GOI (Indo-German Cooperation on Seed Sector Development) |
|
International Training Programme on Plant Variety Protection, Seed Testing and Certification (17-28 Jan, 2020) |
5 |
Kenya Plant Health Inspectorate Service (KEPHIS), Govt. of Kenya |
|
International training cum Capacity Building Programme on “Seed Production and Quality Evaluation” (04-15 Nov, 2019) |
10 |
MoRD, GOI and AARDO |
|
Total |
778 |
|
The Division also started a one-year postgraduate diploma in Seed Science & Technology in 1977 primarily to upgrade the knowledge and skill of the in-service persons from the State Seed Corporations (SSC's) and State Agricultural Universities (SAU's). Fifteen persons who obtained post graduate diploma in seed technology held responsible positions in the seed sector in different SSC's and SAU's. During 1982-1988, a regular Masters' Programme in Seed Science and Technology was started which was again revived in 1992. Ph.D. Programme in Seed Science & Technology was initiated in 1994. The division is offering both M.Sc. and Ph.D degrees in Seed Science and Technology. The number of students admitted for PG programme in the division during the last four years are as follows:
|
Academic Year |
M.Sc. |
Ph.D. |
|
2020-21 |
7 |
7 |
|
2021-22 |
7 |
11 |
|
2022-23 |
8 |
14 |
|
2023-24 |
6 |
13 |
|
Total |
28 |
45 |